
Modern industry relies on Aluminum profiles heavily. The latter are a perfect combination of such properties as lightweight design, supreme strength and exceptional resilience that makes it an ideal fit for various applications starting from sky-scrapes to heavy machinery.
Nevertheless, choosing the right profile among so many options available today could be very challenging. Here is what you need to consider.
The primary consideration in the selection of an industrial aluminum profile is its strength and load-bearing capacity. It should be able to endure both static and dynamic loads that accompany it during its usage period. Different grades of alloys categorize aluminum profiles that have varied mechanical properties.
The required level of strength as well as load bearing capacity determines the choice of alloy. For example, high-strength alloys like 7075 can be used in heavy machinery frames where extraordinary strength is necessary. On the other hand, 6061 may be considered for use in architectural components where there is a delicate balance between formability and strength.
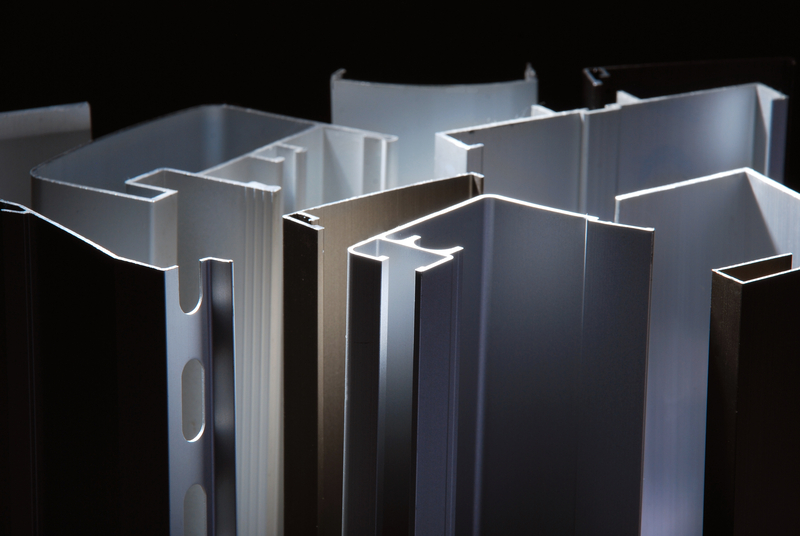
The geometry and cross-sectional shape determine the functionality of an industrial aluminum profile so much so that without one another they cannot exist at all. Today’s discussion is about the shape of profiles. Profiles possess different geometric forms from plain rectangles or squares to complex T-grooves, hollow sections and even made- to –measure ones.
The profile geometries should be selected based on factors such as compatibility with mounting components, ease of assembly, ability for integration with accessories/attachments which are indispensable in particular applications.
For instance, if a modular framing system is being set up then a T-slot profile would be ideal for this purpose while a hollow section is efficient because it is lightweight and uses materials economically.
Aluminum profiles are exposed to harsh environments including industrial areas characterized by chemicals, moisture and extreme temperature conditions. As a result, selecting profiles with good surface treatments that have high resistant to corrosion is crucial.
There are several commonly used procedures that have been employed to ensure that aluminum profiles’ endurance is enhanced and they do not corrode these include anodizing, powder coating and PVDF coating Anodizing creates a thin oxide layer on the surface that offers good resistance against corrosions along with plenty of colors choices.
On the other hand, powder coating gives durable finish that has excellent resistance against abrasion as well as ultra violet rays. On the other hand, PVDF coating is suitable for challenging environments requiring outstanding weather resistance and color retention such as building facades in coastal areas.
In applications where heat dissipation is a critical concern, the thermal conductivity of the industrial aluminum profile becomes a vital factor. Being a great hear conductor, Aluminum enables efficient removal of heat from sensitive components or working areas.
Choosing profiles with high thermal conductivity can help to keep the optimal operating temperatures which make tools or systems last longer.
The lightweight nature of aluminum profiles is a significant advantage since it results in structures’ and equipment’s reduced weights considerably. In some sectors, where reducing weight is crucial, such as automotive, aerospace, and transportation this fact becomes especially important.
Aluminum profiles provide superior structural efficiency that allows for optimized designs that maximize strength while minimizing material usage thus resulting to savings made on costs incurred by vehicles in terms of fuel consumption as well as overall performance improvement.
This term is aimed at explaining how easy or hard it can be to make a piece of aluminum into a complex structure by cutting, drilling, bending and joining such profiles. Aluminum profiles have good machinability thus facilitating their design flexibilities and production processes.
Is there any need for your application to have precise cuts, welded joints or even assembled through the use of special equipment or techniques? Understanding these fabrication needs will help guide your profile selection. For example, softer tempered profiles may be suitable for projects with intricate bends that require better formability.
In terms of practical considerations, cost-effectiveness as well as availability of industrial aluminum profiles are paramount in any project.
By comparing weight vs strength ratio, longevity and competitive advantage over other materials in terms of pricing generally outweighs other related factors when it comes to aluminum profiles as a whole. Nevertheless, some manufacturers or suppliers might not provide certain types like custom or specialized designs.
By considering the factors we have discussed above one can make informed decision when choosing industrial aluminum profiles. Not only will an ideal profile meet your projects’ functional requirements but also ensure that its performance is optimized while durability maintained.
Shishan Production Base
Nonferrous Metal Industrial Park, Xiaotang, Shishan Town, Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Gaobian production base
Gaobian Zhangbian Industrial Zone, Dali Guangyun Road, Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province
Company summary: + 86-757-85558828
Fax: + 86-757-85550238